Security Operations Center (SOC) Training & Certification in Massachusetts
Unlock your career potential with CareerMaker Solutions’ comprehensive SOC Analyst Training Massachusetts. Our Security Operations Center Training Massachusetts program provides practical knowledge and hands-on experience in threat detection, incident response, and cybersecurity management. Tailored for both beginners and experienced professionals, this training equips you with the essential skills needed to excel in today’s ever-evolving security landscape. Led by experts, our courses feature real-world scenarios, ensuring you gain the expertise necessary to protect critical digital assets. Enroll today and take the next step in advancing your cybersecurity career!
Years in IT training industry
IT professional Trained
Countries
Bootcamps
- TRUSTED BY -










- SOC COURSE HIGHLIGHTS -

SOC Certification Training Highlights with CareerMaker:
Comprehensive Curriculum: Our SOC (Security Operations Center) certification training offers an up-to-date, in-depth curriculum covering critical areas such as threat detection, incident response, security monitoring, and more. This ensures you are well-prepared for real-world cybersecurity challenges.
Hands-on Experience: Gain practical skills through immersive simulations and hands-on labs. These exercises enable you to manage and mitigate security threats effectively in a variety of environments.
Expert Instructors: Learn from experienced cybersecurity professionals who have deep knowledge in SOC operations. Their expert insights and practical guidance will provide you with the skills needed to succeed in your career.
Flexible Learning Options: Choose from online, in-person, and hybrid learning formats, allowing you to tailor your education to fit your schedule and personal learning preferences.
Career Support: Take advantage of career guidance, resume-building workshops, and job placement assistance designed to accelerate your journey toward a successful cybersecurity career.
Industry-Recognized Certification: Earn a SOC certification that is recognized by top organizations in the cybersecurity field. This certification will boost your professional credibility and open doors to exciting career opportunities.
Networking Opportunities: Connect with peers, mentors, and industry experts through our platform, helping you expand your professional network and build valuable connections in the cybersecurity community.
- Upcoming Live BOOTCAMP CALENDAR -
Class Schedule
| 08:00 AM-10:00 AM(EST) | Weekend Evening | October 26 2024 - November 24 2024 | Live Online | $1200 STUDY NOW PAY LATER | INQUIRY NOW |
| 05:00 PM-08:00 PM(CST) | Weekend Evening | October 26 2024 - November 24 2024 | Live Online | $1200 STUDY NOW PAY LATER | INQUIRY NOW |
| 10:00 AM to 06:00PM(CST) | Weekdays | October 07 2024- November 02 2024 | Live Online | $1200 STUDY NOW PAY LATER | INQUIRY NOW |
October 26 2024 To November 24 2024
October 26 2024 To November 24 2024
October 07 2024 To November 02 2024
-Security Operation Center Training Program -
A Security Operations Center (SOC) is a specialized team responsible for managing and addressing an organization's security at both technical and operational levels. The SOC continuously monitors systems, networks, and applications to detect potential security threats and respond to incidents in real-time. The primary goal of a SOC is to protect the organization's digital assets by proactively defending against security breaches, cyberattacks, and other cyber threats. Through continuous vigilance, the SOC ensures that the organization can identify, respond to, and mitigate risks, maintaining the security and integrity of its operations.
Continuous Monitoring: The SOC team continuously monitors the organization's systems, networks, and applications to detect and analyze any suspicious activity or emerging threats in real time, ensuring timely intervention.
Incident Detection and Response: When security incidents are identified, the SOC responds promptly to contain and mitigate the impact, minimizing potential damage and ensuring a swift recovery.
Utilizing Threat Intelligence: By integrating both internal and external threat intelligence, the SOC gains valuable insights to anticipate and proactively defend against emerging threats, strengthening the organization's cybersecurity posture.
Vulnerability Management: The SOC identifies, prioritizes, and addresses vulnerabilities within systems and infrastructure, implementing remediation strategies to prevent exploitation and reduce the risk of cyberattacks.
Compliance Management: The SOC ensures that the organization adheres to relevant security regulations and industry standards, helping mitigate the risk of non-compliance penalties and fostering trust with clients and stakeholders.
Cyber threats encompass a wide range of risks, including:
Malware: Malicious software created to damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to systems. This includes viruses, worms, ransomware, and spyware that can compromise data and cause system failures.
Phishing Attacks: Fraudulent attempts to acquire sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, or personal data by impersonating legitimate organizations. These attacks typically occur via email, websites, or phone calls designed to deceive victims.
Ransomware: A type of malware that locks or encrypts a victim's data, demanding payment to restore access. It can disrupt business operations and cause significant financial loss.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: Attempts to overwhelm systems, networks, or websites with traffic to make them unavailable to users, often causing operational disruptions.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Extended, targeted attacks where cybercriminals gain unauthorized access to networks and maintain control over a long period to steal data or monitor activities.
Insider Threats: Security risks originating from individuals within the organization, whether intentional or accidental, who may exploit access to sensitive information.
SQL Injection: A type of attack where malicious SQL code is injected into an input field to gain unauthorized access to databases, compromising sensitive data.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: Cyberattacks where attackers intercept or alter communications between two parties to steal data or inject malicious content.
The Security Operations Center (SOC) employs a range of advanced tools to effectively detect, analyze, and respond to cybersecurity threats. Key tools include:
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): These systems monitor network traffic for unusual activity and known threats. When suspicious behavior is detected, IDS alerts the SOC team, allowing them to identify and respond to potential breaches promptly.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: SIEM platforms aggregate and analyze security data from across the network in real-time. By correlating logs and events from various sources, SIEM systems enable the SOC to track threats, detect patterns, and respond to incidents quickly and efficiently.
Threat Intelligence Platforms: These platforms provide the latest information on emerging threats, vulnerabilities, attack vectors, and cybersecurity trends. By integrating external and internal threat intelligence, SOC teams can anticipate new risks and develop proactive defense strategies to mitigate them.
When a breach occurs, a Security Operations Center (SOC) follows a systematic and structured approach to manage and mitigate the impact:
Identification: The first step is identifying the breach. SOC analysts examine security alerts, logs, and threat intelligence feeds to assess the scope and nature of the incident, allowing them to determine the severity and affected systems.
Containment: To prevent the breach from spreading further, the SOC isolates the compromised systems or network segments. This containment step minimizes the potential damage and stops the attack from impacting other parts of the network.
Eradication: Once containment is established, the SOC works to eliminate the root cause of the breach. This may involve removing malware, patching vulnerabilities, and fixing any compromised systems to ensure that the threat is fully neutralized.
Recovery: After eradicating the threat, the SOC focuses on restoring systems and data to normal operation. This includes validating the integrity of the systems, ensuring that there are no lingering issues, and monitoring for signs of re-infection or recurrence.
Request for More Information
-SOC Certification Syllabus -
Security Operations Center (SOC) Training Curriculum
1. Introduction to Security Operations Centers (SOC)
- Overview of SOC Functions and Structure: Understand the critical functions of a SOC, including continuous monitoring, threat detection, incident response, and vulnerability management. Learn the structure of a SOC, including roles and responsibilities.
- Importance of SOC in Cybersecurity: Learn why SOCs are pivotal in safeguarding an organization’s digital infrastructure and managing cyber risks in real-time.
2. Security Frameworks and Compliance
- Understanding Regulatory Requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA): Gain an understanding of major cybersecurity regulations and compliance requirements, such as GDPR and HIPAA, and how they shape SOC operations.
- Compliance Frameworks and Best Practices: Explore key cybersecurity frameworks such as NIST, ISO 27001, and CIS, and learn how to implement best practices for maintaining compliance.
3. Threat Detection and Analysis
- Types of Cyber Threats and Attack Vectors: Learn about various cyber threats, such as malware, phishing, DDoS attacks, and insider threats. Understand how different attack vectors work.
- Anomaly Detection Techniques: Explore techniques for detecting anomalies in network traffic, user behavior, and system activities, which may indicate potential security incidents.
- Using Threat Intelligence to Enhance Security: Learn how to integrate external and internal threat intelligence to proactively identify and mitigate emerging threats.
4. Incident Response Process
- Incident Response Planning and Preparation: Develop an understanding of how to plan and prepare for cybersecurity incidents, ensuring quick and effective action.
- Steps in the Incident Response Lifecycle: Learn the critical phases of incident response, including identification, containment, eradication, and recovery.
- Tools and Methodologies for Effective Response: Familiarize yourself with tools and methodologies used in incident response, including SIEM platforms, forensic analysis tools, and communication protocols.
5. Security Monitoring and Logging
- Setting up Monitoring Systems and Alerts: Learn how to establish effective monitoring systems, configure alerts, and ensure that the SOC can detect threats in real-time.
- Log Management and Analysis: Understand the importance of log collection, management, and analysis in detecting security incidents and understanding attack patterns.
- Use of Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: Dive into SIEM tools, understanding how they aggregate, correlate, and analyze data from across the network to detect security events.
6. Vulnerability Management
- Identifying and Assessing Vulnerabilities: Learn methods to identify vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and applications, and assess their potential risk to the organization.
- Tools for Vulnerability Scanning: Understand the role of vulnerability scanning tools in identifying security gaps and assessing system weaknesses.
- Remediation Strategies: Learn strategies for remediating vulnerabilities, including patch management, configuration management, and the prioritization of fixes.
7. Hands-on Labs and Simulations
- Real-World Simulations of Security Incidents: Participate in live, hands-on simulations that replicate real-world cyberattacks, allowing you to respond in a controlled environment.
- Practical Exercises in Threat Detection and Response: Engage in practical exercises that teach you how to detect, analyze, and respond to various types of security incidents.
8. Emerging Threats and Trends
- Analysis of Recent Cyber Threats and Trends: Study the latest cybersecurity threats, attack methods, and trends in the cyber threat landscape.
- Future Challenges in Cybersecurity: Gain insights into the future of cybersecurity, understanding emerging technologies and evolving attack tactics.
9. Career Development in SOC
- Building a Career in Cybersecurity: Learn about career pathways in the cybersecurity field, specifically within SOC operations.
- Resume Building and Interview Preparation: Receive guidance on how to build an effective resume and prepare for interviews in the cybersecurity industry.
- Networking and Professional Development Opportunities: Learn how to leverage networking opportunities and professional organizations to advance your career.
10. Capstone Project
- Final Project Integrating All Learned Concepts: Apply all of the skills and knowledge gained throughout the program in a final capstone project that demonstrates your ability to respond to a comprehensive security scenario.
- Presentation and Evaluation of the Project: Present your project findings and solutions to a panel of instructors and industry professionals for evaluation.
-SOC Certification Job & Salary -

Common tools utilized in a Security Operations Center (SOC) are crucial for detecting, analyzing, and responding to security threats effectively. These include:
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: SIEM platforms aggregate and analyze data from various sources to provide real-time visibility into security events, helping SOC teams identify and respond to potential threats quickly.
Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): IDS/IPS tools monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and known attack patterns, enabling the SOC to detect and prevent unauthorized access or potential breaches.
Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks, blocking malicious traffic while allowing legitimate communication to pass through.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Systems: EDR tools focus on monitoring, detecting, and responding to threats on endpoints, such as workstations and servers. These tools help in identifying malicious activities and contain threats before they spread.
Network Monitoring Tools: These tools continuously monitor network activity to detect anomalies, bottlenecks, and security threats, providing real-time insights into network health and potential risks.
Common tools utilized in a Security Operations Center (SOC) are crucial for detecting, analyzing, and responding to security threats effectively. These include:
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: SIEM platforms aggregate and analyze data from various sources to provide real-time visibility into security events, helping SOC teams identify and respond to potential threats quickly.
Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): IDS/IPS tools monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and known attack patterns, enabling the SOC to detect and prevent unauthorized access or potential breaches.
Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks, blocking malicious traffic while allowing legitimate communication to pass through.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Systems: EDR tools focus on monitoring, detecting, and responding to threats on endpoints, such as workstations and servers. These tools help in identifying malicious activities and contain threats before they spread.
Network Monitoring Tools: These tools continuously monitor network activity to detect anomalies, bottlenecks, and security threats, providing real-time insights into network health and potential risks.
Threat intelligence is the process of gathering, analyzing, and leveraging information about current and emerging cyber threats to enhance an organization's security posture. By providing insights into potential vulnerabilities, attack patterns, and tactics used by cybercriminals, threat intelligence helps organizations understand the ever-evolving threat landscape.
This critical data enables security teams to take proactive measures to prevent or mitigate cyberattacks before they can inflict damage, such as:
Identifying Emerging Threats: Early detection of new threats or attack vectors allows organizations to adjust their defense mechanisms promptly.
Improving Threat Detection: Threat intelligence enhances the ability to identify suspicious activity by providing up-to-date information on known malicious indicators.
Strengthening Incident Response: With actionable intelligence, SOC teams can respond to incidents more effectively by knowing the nature of the attack and the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by adversaries.
Threat intelligence significantly enhances Security Operations Center (SOC) operations by providing critical insights that inform various key processes, including threat detection, incident response, and vulnerability management. Here's how threat intelligence supports each of these functions:
Threat Detection: By analyzing data from external sources, threat intelligence helps SOC teams recognize patterns and indicators of compromise (IOCs) related to known and emerging threats. This enables the SOC to proactively monitor for suspicious activities and detect threats earlier in the attack lifecycle.
Incident Response: When a security incident occurs, threat intelligence provides essential context that allows SOC teams to respond more effectively. By understanding the attack's characteristics, such as the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by adversaries, SOC teams can quickly implement the appropriate response measures, minimizing the impact and preventing further damage.
Vulnerability Management: Threat intelligence also aids in vulnerability management by identifying vulnerabilities that are actively being exploited by cybercriminals. With this knowledge, SOC teams can prioritize patching and remediation efforts to address weaknesses before they are exploited in an attack.
Vulnerability management is a critical process within a Security Operations Center (SOC), aimed at identifying, assessing, and mitigating weaknesses within an organization's IT infrastructure. The process typically includes the following steps:
Identification: Vulnerabilities are discovered through regular scans, penetration testing, and monitoring of systems, networks, and applications. This helps identify any security gaps that could be exploited by attackers.
Assessment: Once identified, vulnerabilities are assessed to determine their severity and potential impact on the organization. This involves evaluating the risk each vulnerability poses based on factors like exploitability, the value of the affected system, and the potential consequences of an attack.
Mitigation: After assessing vulnerabilities, SOC teams prioritize them based on severity and implement strategies to reduce or eliminate the risks. These strategies may include applying patches, reconfiguring systems, strengthening network defenses, or removing vulnerable software.
Continuous Monitoring: Vulnerability management is an ongoing process. SOC teams continuously monitor systems for new vulnerabilities and assess the effectiveness of mitigation efforts to ensure the organization's infrastructure remains secure over time.
Compliance within a Security Operations Center (SOC) is essential for ensuring that an organization meets the necessary legal, regulatory, and industry-specific security standards. By aligning SOC operations with frameworks such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and other relevant regulations, the SOC ensures that sensitive data is protected, privacy is maintained, and security practices are in line with legal requirements.
Key aspects of compliance in a SOC include:
Data Protection: Ensuring sensitive data, including personal, financial, and health-related information, is handled securely according to regulatory requirements like GDPR or HIPAA. This involves implementing encryption, access controls, and data retention policies.
Incident Reporting: Compliance regulations often require specific protocols for incident detection, reporting, and response. For example, GDPR mandates that breaches be reported within 72 hours, so SOCs must have processes in place for swift identification and communication of security incidents.
Access Control and Monitoring: Regulations often specify strict access control measures to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data or systems. SOCs must implement and enforce these access controls and regularly monitor user activities.
Audit and Documentation: Compliance requires thorough record-keeping and auditing of security operations. SOC teams must maintain detailed logs and reports of security activities, ensuring transparency and accountability in their operations.
Continuous Risk Assessment: Regulatory frameworks require ongoing risk assessments and vulnerability management to identify potential risks and take proactive measures to address them. SOCs need to regularly review systems and policies to ensure compliance with evolving standards.
Security Operations Centers (SOCs) generate several types of reports that provide crucial insights into the organization's cybersecurity posture and operations. These reports play a pivotal role in identifying trends, improving defense strategies, and ensuring compliance with regulations. The key reports include:
Incident Reports: These reports document detailed information about security incidents, such as the type of breach (e.g., malware, DDoS attack), the systems affected, the timeline of events, actions taken during the incident response, and the resolution. Incident reports help SOC teams analyze what went wrong, identify weaknesses in the security infrastructure, and take steps to prevent similar incidents in the future.
Compliance Reports: SOCs create reports that confirm adherence to industry regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS). These reports include an assessment of how the organization is complying with specific security requirements, detailing the measures implemented to protect data, maintain privacy, and meet regulatory deadlines. Compliance reports are essential for audits, legal purposes, and ensuring that the organization meets mandatory security standards.
Threat Analysis Reports: These reports focus on identifying emerging threats, attack vectors, and potential risks that could compromise the organization's security. SOC teams gather data on new vulnerabilities, malware trends, and attack patterns. These insights help to inform proactive defense strategies, enabling organizations to strengthen their systems before a potential threat becomes a real attack.
Executive Summaries: These high-level reports provide senior management with an overview of the organization's security posture, highlighting key incidents, vulnerabilities, mitigation efforts, and ongoing security initiatives. Executive summaries are designed to give decision-makers a quick but comprehensive understanding of the organization's cybersecurity health and areas that require attention, enabling informed decisions about resource allocation and strategic direction.
To ensure effective operations and enhance cybersecurity capabilities, Security Operations Centers (SOCs) should implement the following best practices:
Regular Staff Training: Continuously educate SOC personnel on the latest cybersecurity threats, tools, and attack methodologies. Regular training ensures that SOC staff is equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats. This includes training on the latest attack vectors, defensive technologies, and incident response protocols.
Automated Monitoring Tools: Leverage automation to streamline threat detection and incident response processes. Automated tools, such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions, can significantly reduce the time it takes to detect and respond to threats. Automation allows SOC teams to focus on higher-priority tasks and more complex incidents, improving operational efficiency and reducing human error.
Up-to-Date Threat Intelligence: Regularly update and integrate threat intelligence feeds into the SOC's monitoring and response protocols. By staying current on emerging threats, attack tactics, vulnerabilities, and malware trends, SOCs can proactively adjust their security measures to defend against new risks. This ensures a more informed and dynamic defense strategy, capable of mitigating even the latest cybersecurity threats.
Routine Security Audits: Conduct frequent security audits and assessments to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses within the organization's systems. These audits evaluate the effectiveness of current security measures, ensure compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA), and help improve overall cybersecurity posture. Regular assessments provide an opportunity to fix gaps, update security controls, and maintain a strong defense against evolving threats.
To further enhance the effectiveness of a Security Operations Center (SOC), the following advanced strategies should be implemented:
Integrating Advanced Analytics: Leverage data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance threat detection and response. These technologies can analyze large volumes of security data, identify patterns, detect anomalies, and predict potential threats with greater accuracy and speed. Machine learning algorithms, for example, can continuously learn from past incidents to improve future threat identification, while AI can automate the process of identifying and responding to suspicious activity in real time.
Adopting Automation: Automate routine SOC tasks such as log analysis, threat detection, and incident response workflows. By automating these tasks, SOC analysts can focus on more complex and high-priority issues, improving efficiency and reducing the time spent on manual tasks. Automation can also reduce the risk of human error, allowing for faster response times and more consistent security measures.
Promoting a Strong Security Culture: Foster a security-conscious culture throughout the organization by continuously educating employees at all levels on security best practices. This includes providing regular training on topics like phishing awareness, secure password management, and safe use of company systems. Encourage collaboration across departments to ensure that everyone is aligned with the organization’s security policies and practices. A strong security culture enhances vigilance, reduces insider threats, and improves overall security awareness.
Continuously Updating Processes and Tools: Regularly review and update SOC processes, tools, and technologies to keep pace with evolving cyber threats. As cyberattacks become more sophisticated, it’s crucial for SOCs to stay ahead of emerging risks by adopting new tools, refining incident response protocols, and ensuring the effectiveness of threat detection systems. This can include upgrading SIEM platforms, integrating new endpoint protection technologies, and revising incident response plans based on lessons learned from previous incidents. Continuous improvement ensures the SOC remains adaptable and ready to handle new challenges.
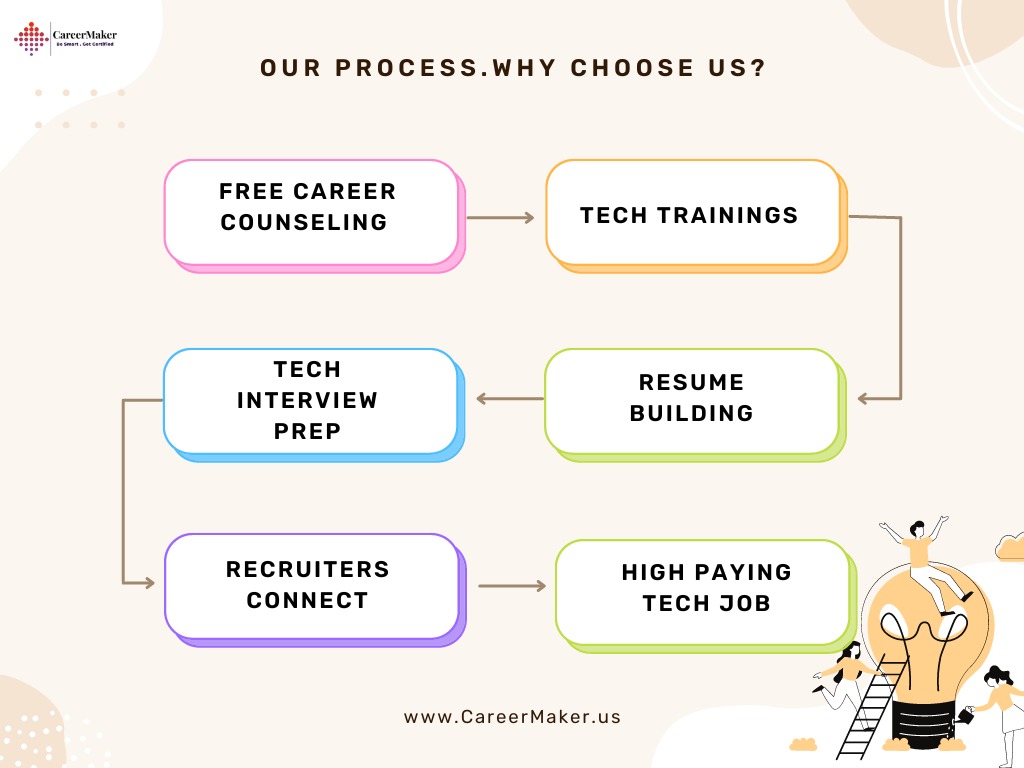
- Benefits Of Choosing CareerMaker Solutions ? -
- Our World-Class CERTIFIED INSTRUCTIOR
As a SOC Analyst at Specialty Solutions, I apply my expertise in cyber threat hunting (CTH) and Splunk Enterprise Security (ES) to monitor, detect, and respond to cyber incidents. I work with a team of cybersecurity professionals to protect the company's network and systems from malicious actors and ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations. I have multiple years of experience in the cybersecurity field, having previously worked as a Security Engineer at SecureTech, where I developed and implemented security solutions and policies. I have also acquired multiple certifications and skills in CTH, Splunk ES, and cybersecurity incident response, which enable me to perform my role effectively and efficiently. I am passionate about cybersecurity and always eager to learn new technologies and techniques to enhance my knowledge and skills
Nim Fon Queenette.
SOC Instructor- Certification Of Course Completion -

- Success Stories -
ARE YOU READY TO TAKE YOUR CYBER SECURITY CAREER TO THE NEXT LEVEL -
Don’t miss the opportunity to advance your cybersecurity career with our comprehensive Security Operation Center certification training. Enroll today and gain the essential skills and knowledge needed to protect organizations from the ever-growing landscape of cyber threats.
Contact us now to discover more about our training program, course schedules, and enrollment options. Start your path to a rewarding career in cybersecurity today!

- FAQ -
To further enhance the effectiveness of a Security Operations Center (SOC), the following advanced strategies should be implemented:
Integrating Advanced Analytics: Leverage data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance threat detection and response. These technologies can analyze large volumes of security data, identify patterns, detect anomalies, and predict potential threats with greater accuracy and speed. Machine learning algorithms, for example, can continuously learn from past incidents to improve future threat identification, while AI can automate the process of identifying and responding to suspicious activity in real time.
Adopting Automation: Automate routine SOC tasks such as log analysis, threat detection, and incident response workflows. By automating these tasks, SOC analysts can focus on more complex and high-priority issues, improving efficiency and reducing the time spent on manual tasks. Automation can also reduce the risk of human error, allowing for faster response times and more consistent security measures.
Promoting a Strong Security Culture: Foster a security-conscious culture throughout the organization by continuously educating employees at all levels on security best practices. This includes providing regular training on topics like phishing awareness, secure password management, and safe use of company systems. Encourage collaboration across departments to ensure that everyone is aligned with the organization’s security policies and practices. A strong security culture enhances vigilance, reduces insider threats, and improves overall security awareness.
Continuously Updating Processes and Tools: Regularly review and update SOC processes, tools, and technologies to keep pace with evolving cyber threats. As cyberattacks become more sophisticated, it’s crucial for SOCs to stay ahead of emerging risks by adopting new tools, refining incident response protocols, and ensuring the effectiveness of threat detection systems. This can include upgrading SIEM platforms, integrating new endpoint protection technologies, and revising incident response plans based on lessons learned from previous incidents. Continuous improvement ensures the SOC remains adaptable and ready to handle new challenges.
In this program, participants will immerse themselves in real-world scenarios, including simulated cyberattacks and incident response exercises, to apply their skills in a practical, hands-on environment. They'll gain firsthand experience in managing and responding to security incidents, honing their ability to detect, analyze, and mitigate threats effectively.
Additionally, participants will develop Python scripts to automate routine SOC tasks, such as log analysis, threat detection, and incident response workflows. This will not only streamline operations but also enhance their ability to analyze security data, identify vulnerabilities, and respond to emerging threats efficiently. By combining theoretical knowledge with practical exercises, participants will strengthen their skills and improve their overall security management capabilities, preparing them for success in the dynamic and demanding field of cybersecurity.
The program offers a balanced approach by combining theoretical knowledge with hands-on practice, enabling you to apply learned concepts to real-world cybersecurity scenarios. Through practical exercises, you'll gain valuable experience with industry-standard tools and technologies, preparing you to tackle and mitigate complex security threats in a professional SOC environment. This experiential learning will equip you with the skills needed to navigate dynamic cybersecurity challenges, ensuring you’re well-prepared to make an immediate impact in the field.
Upon successful completion of the program, you will receive a certification that recognizes your expertise as a Master SOC Analyst. This certification will validate your advanced skills and capabilities in security operations, positioning you as a highly qualified professional in the cybersecurity field. It will enhance your career prospects, making you a valuable asset to potential employers seeking skilled individuals to protect their digital infrastructure from emerging cyber threats.
While prior experience in cybersecurity or programming can be beneficial, it is not required. The program is designed to cater to both beginners and seasoned professionals. For newcomers, it provides a strong foundation in cybersecurity concepts, while for those with experience, it offers advanced knowledge and the opportunity to refine and expand their skills. This flexible approach ensures that all participants can build their expertise and grow at their own pace, regardless of their starting point.
While prior experience in cybersecurity or programming can be beneficial, it is not required. The program is designed to cater to both beginners and seasoned professionals. For newcomers, it provides a strong foundation in cybersecurity concepts, while for those with experience, it offers advanced knowledge and the opportunity to refine and expand their skills. This flexible approach ensures that all participants can build their expertise and grow at their own pace, regardless of their starting point.
The Master SOC Analyst Training Program provides you with the advanced skills and certification needed to stand out in the competitive cybersecurity job market. By mastering Python programming and gaining hands-on experience with critical tools, you’ll be fully prepared to excel in high-level SOC roles and accelerate your career in cybersecurity.


